Pipe hangers, are commonly known as “piping supports” or “pipe hangers”. They play a strategic role in ensuring the structural integrity and long-term functionality of an industrial plant. These components are in fact indispensable elements of the entire piping system, designed to support, anchor, guide and protect piping lines against dynamic and static forces that can compromise the safety and efficiency of the plant.
Pipe supports, in fact, perform multiple functions: from simple physical support to the control of vibrations induced by the flow of fluids, from the compensation of thermal expansion to the prevention of structural damage due to excessive loading. Understanding these aspects is essential for those working in the plant engineering sector, as an inadequate choice or incorrect design can lead to plant failures, unplanned downtime and, in the worst case, accidents, with serious consequences on the safety of people and the environment.
Through this guide we will discover in detail what pipe supports are and what they are used for. It highlights the main stresses to which pipes are subjected and the most suitable design methods to ensure maximum efficiency and safety.
What are piping supports?
As anticipated, pipe supports are structural components designed to support, anchor, guide and protect pipes. These elements have the task of absorbing and distributing the loads deriving from the self-weight of the pipes, the fluid in transit, thermal variations, vibrations and any external stresses, such as wind or seismic movements.
Their function is therefore twofold: on the one hand, they ensure that the pipes maintain the correct position, preserving them from any deformation; on the other hand, they contribute to the overall safety of the plant, reducing the risk of accidents caused by material leakage or structural failure. Pipes, in fact, are subjected to different types of stresses: primary loads (the internal pressure of the pipe, external pressure and forces due to the loading and unloading of the fluid) and secondary loads, due to thermal expansion and the effects caused by earthquakes and atmospheric events.
The loading conditions of the pipes will be analyzed during the piping stress analysis, the study of the stresses and deformations to which the piping line is subjected.
Main types of pipe support
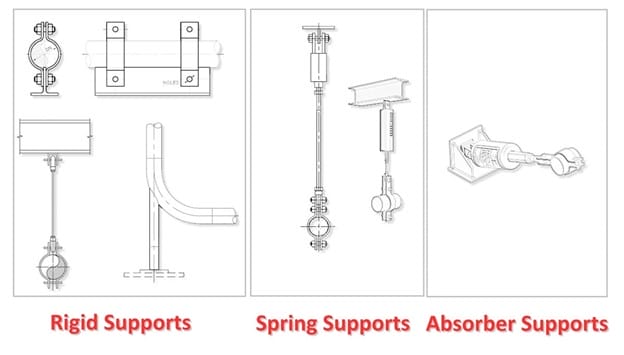
The correct selection and installation of piping supports is essential to ensure the safety and efficiency of the entire piping line. Below, we explore the main types available, highlighting their characteristics and contexts of use.
- Rigid. Designed to provide a fixed point capable of supporting the weight of the pipe, limiting movements caused, for example, by external factors. Among the most common are rod hangers, consisting of a clamp, an eye nut, a tie rod and a beam attachment; the Stanchion/Pipe Shoe, designed to support the pipes, from above or below, limiting their movement in any direction of rotation. In addition, there are also rigid struts, the connections between a piping system and a support structure that provide fixed and stable support, limiting horizontal and vertical movements and absorbing mechanical stress without allowing significant bending.
- Spring-loaded. Composed of compression springs that allow you to manage the vertical movements of the pipes caused by thermal expansion: they ensure a certain degree of movement while providing the necessary support. Examples include variable spring supports (VES), used for piping lines subject to moderate vertical thermal movements (top plate, pressure and bottom plate, helical spring, locking rods, etc.) and constant spring supports (CES), used in cases where large vertical movements occur (150 or 250 mm).
- Shock absorbers. Also known as “snubbers”, they are devices composed of a mechanical part equipped with a spring combined with a hydraulic element: they are used to protect the pipes from vibrations or water hammer. This includes dynamic restraints, such as hydraulic and mechanical snubbers and insulated pipe supports, designed to minimize energy dissipation.
Understanding the functionality and possible applications of these components is essential for those who work in the field of design and maintenance of industrial plants. The choice of the type that best suits your needs allows you to meet the different operational and safety needs of the system.
How to design pipe support?
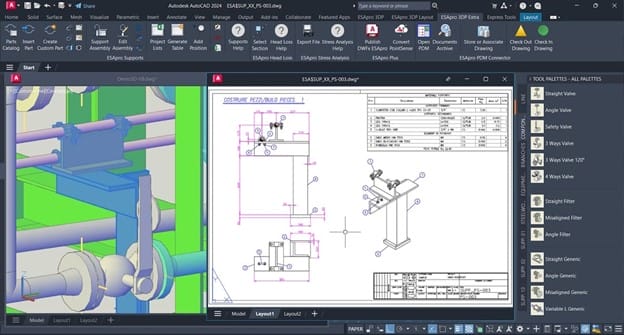
The design of piping supports is a critical element in industrial plant engineering. It ensures the safety, efficiency and durability of the entire pipe line.
The first step in the design of pipe supports is the stress analysis: an accurate evaluation of these forces is crucial to determine the type that best suits your needs. Their design must also comply with industry regulations and standards, which define safety requirements, calculation procedures, and design criteria.
For these reasons, ad hoc solutions are available designed to design pipe supports in 3D, which also allow you to extract the necessary construction drawings and bills of materials. One of the best solutions is ESAin’s ESApro Supports module. It includes a wide library of customizable three-dimensional parts: from attachments (collars, U-bolts, etc.) to supports (shoes, guides, springs, etc.) to fasteners and carpentry elements (bolts, tie rods, beams, plates, etc.).
After assembling the different parts, the software also allows grouping into assemblies, which are associated with specific properties, such as the type (axial or lateral guide, etc.), the progressive number and the connected lines. Finally, to facilitate the construction of pipe supports, the software allows you to generate 2D drawings containing the exact position and any dimensions.
Do you want to know more? Contact us !
Francesco Pais initially wrote this post on April 3rd
